Kagoshima Galactic Object Survey With Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope by Mapping in Ammonia Lines
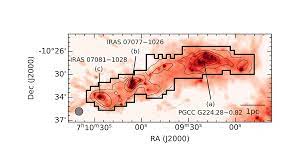
The universe has always fascinated us with its vastness and mysteries. In our quest to understand the cosmos, astronomers and researchers utilize cutting-edge technology, such as the Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope, to explore and map galactic objects. One remarkable survey conducted with this telescope is the Kagoshima Galactic Object Survey, which focuses on mapping in ammonia lines, unraveling the secrets hidden within our galaxy.
Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope: A Marvel in Astronomy
Historical Background of the Telescope
The Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope has a rich history, dating back to its inception in the early days of modern astronomy. Originally designed for specific observations, it has evolved into a versatile instrument that plays a crucial role in contemporary astronomical research.
Technical Specifications and Capabilities
Boasting a massive 45-meter dish, the telescope enables astronomers to capture detailed observations of celestial bodies. Its advanced technology allows for precise measurements and data collection, making it an indispensable tool in the pursuit of unraveling the mysteries of the universe.
Ammonia Lines: Unveiling Galactic Mysteries
The Importance of Ammonia Lines in Astronomy
Ammonia lines serve as valuable markers in the vastness of space. Astronomers leverage these lines to study the composition, temperature, and movements of interstellar gas clouds. Mapping in ammonia lines provides a unique perspective, offering insights that are crucial for understanding the dynamics of our galaxy.
Insights Provided by Mapping in Ammonia Lines
By employing the Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope to map in ammonia lines, researchers can peer into regions of space that were once obscured. This mapping technique unveils the intricate details of galactic objects, helping astronomers decipher the complex interplay of forces shaping our cosmic neighborhood.
…
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Kagoshima Galactic Object Survey, conducted with the remarkable Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope, has significantly contributed to our understanding of the cosmos. Through meticulous mapping in ammonia lines, astronomers have unveiled hidden mysteries, making groundbreaking discoveries that resonate across the field of astrophysics.
FAQs
- What makes the Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope unique in astronomy?
- The telescope’s historical significance and advanced technical capabilities set it apart, enabling precise observations crucial for various astronomical studies.
- How do ammonia lines contribute to mapping galactic objects?
- Ammonia lines serve as valuable indicators, allowing astronomers to study the composition and dynamics of interstellar gas clouds, providing a deeper understanding of the cosmos.
- What challenges did the Kagoshima Galactic Object Survey face, and how were they overcome?
- The article discusses challenges faced during the survey and highlights the innovative solutions implemented by the research team.
- What real-world applications have emerged from the survey findings?
- Beyond astronomy, the article explores unexpected applications and societal benefits arising from the Kagoshima Galactic Object Survey.
- What are the future prospects for the Nobeyama 45-metre Telescope and upcoming surveys?
- The article outlines plans for future surveys, improvements to the telescope, and its expanding role in advancing astronomical research.





